Blog / What is Post-Secondary Education in Canada? A Comprehensive Guide
What is Post-Secondary Education in Canada? A Comprehensive Guide

Explore our Diploma Programs
- Business, Hospitality, and Legal
- Health and Human Services
- Technology
Table of Contents
What is post-secondary education in Canada? It’s the next step after high school (or equivalent), offering pathways like universities, colleges, and polytechnics. The right post-secondary school is key to career growth – it can determine factors such as better job opportunities, higher earning potential, and long-term career stability.
Career-focused colleges, in particular, stand out by offering personalized training, hands-on learning, and programs tailored to in-demand careers in today’s job market, helping you enter the workforce quickly and confidently.
While all options have their merits, what matters is learning about each of them and finding which path to post-secondary is the best fit for you.
Listen to: What is Post-Secondary Education in Canada? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Post-Secondary Education
Before you enter the next phase of your education, whether you’ve just graduated high school, just arrived in Canada, or are simply looking to return to education to brush up your skills for your next career move, it’s important to understand what post-secondary is all about.
By knowing exactly what types of post-secondary education are available to pursue – like universities, colleges, and polytechnics– you can pick the path that aligns with your goals.
Definition of Post-Secondary Education
Post-secondary education (higher or tertiary education) includes all formal education and training after high school, which is known as secondary education. In Canada, high school (grades 8–12, varying by province) builds a foundation in core subjects like math, science, and language.
From here, you have plenty of options to continue building your skills and experience. Post-secondary education provides you an advantage that helps you compete in today’s job market. A background in post-secondary education is more important than ever to employers, with over 50% of new jobs requiring post-secondary credentials. Each type of post-secondary education offers a unique learning approach that can impact how you build and apply your skills in the workforce – which is why choosing the right one matters.
Post-secondary education can support long-term success, but outcomes vary based on the type of program, industry demand, and how well training aligns with employer needs.
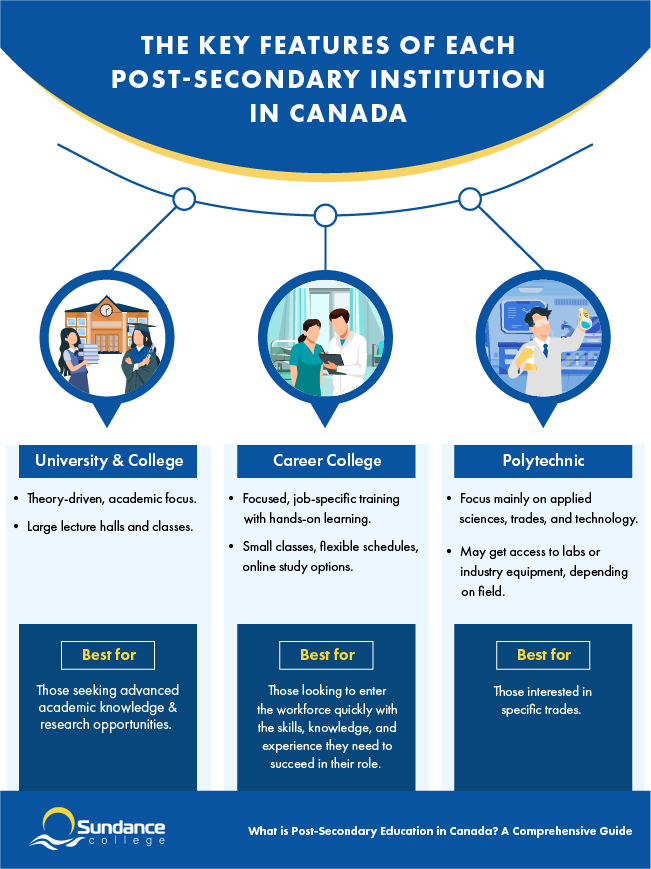
Types of Post-Secondary Institutions
While the importance of post-secondary education cannot be overstated, it’s just as important to know the options available to you. Each type of post-secondary institution offers unique learning approaches and programs tailored to different goals.
Here’s what you can expect from each of them:
University & College
Universities are known for their academic and theory-driven approach to education. What exactly does that mean? Here’s what you can expect from higher learning in a university:
Approach to Learning
Think lectures, essays, and research papers. University aims to help you develop critical thinking and independent learning skills through theory.
Type of Learning Environment
While students can have access to extensive research facilities, it’s important to note that most learning is done in large lecture halls. This means large class sizes and a generic learning experience.
Programs & Credentials
University offers a wide range of programs, covering everything from introductory courses to advanced, specialized topics. In fields like arts, sciences, engineering, and medicine, universities can award you with a degree, which include the following:
- Bachelor’s Degree: A foundational program that provides specialized knowledge, typically completed in 4-5 years.
- Master’s Degree: An advanced program for further specialization, requiring an additional 1-3 years after a bachelor’s degree.
- Doctoral Degree: The highest level of academic achievement, involving 3-4 years of intensive study and research after completing a master’s degree.
A university program may be a good fit if you’re interested in research, long-term academic study, or careers that require advanced degrees. Some university paths prepare you for a career in about four years – like nursing or teaching – but others, such as becoming a lawyer, or professor, require six or more years of study before you can even begin working in your field.
Career College
Career colleges specialize in short-term, targeted training programs designed to prepare you to enter the workforce in a specific occupation. Unlike universities and colleges, you can expect a focused, flexible, and faster approach to post-secondary education – and employment! Here’s how career colleges do it:
Approach to Learning
- Relevant Training: Career college programs are designed to teach only the skills needed for specific jobs, cutting out unnecessary coursework.
- Hands-On Learning: Career college diploma programs emphasize practical skills through workshops, specially designed labs, practicums, and practical assignments that mirror real-world tasks.
- Fast-Tracked Programs: Most programs take between six months and a little over a year to complete, allowing you to enter the workforce quicker than any other post-secondary option.
Type of Learning Environment
- Flexible Scheduling: With flexible scheduling, career colleges make it possible to balance education with work, family, and other commitments. Depending on your program, it’s possible to set yourself up for success in a career college by fully completing your studies online.
- Industry-Ready: Students at career colleges graduate with immediately useful skills in programs that are tailored to current market needs.
- Small Class Sizes: Smaller class sizes in career colleges offer the kind of focused, supportive learning environment with personalized attention from instructors that benefits all students.
Programs & Credentials
- Focus on In-Demand Fields: Career colleges provide diverse programs across many in-demand industries, including healthcare, business, technology, legal studies, hospitality, and supply chain management—fields with some of the best career opportunities in Canada.
- Same Credentials but Sooner: One of the biggest benefits of a diploma from a career college is the ability to complete it in less time than other colleges, thanks to efficient, job-focused training. Instead of studying for years, you can complete your studies between six months to a little over a year.
By offering specialized training in a shorter time frame, career colleges enable you to gain not only the qualifications, but the skills, knowledge, industry experience, and career support you need to enter the workforce faster than traditional education paths—without sacrificing quality or support.
Polytechnics
Polytechnics offer a mix of classroom instruction and practical training, mainly in areas like applied sciences, trades, and technology. Programs often include co-ops, internships, or apprenticeships, so students gain hands-on experience in labs or industry equipment, depending on their field. Credentials range from certificates to applied degrees, generally preparing students for technical roles in sectors like IT, engineering, or skilled trades.
Post-Secondary Education in Canada
Understanding Canada’s Post-Secondary Education System
You deserve a high quality post-secondary education – and making sure the institution you choose is government-recognized is a key part of that. In Canada, the responsibility for recognizing post-secondary institutions and their programs lies with provincial and territorial governments. Each province or territory has its own ministry or department overseeing education, so institutions meet specific standards before they’re allowed to offer degrees, diplomas, and other credentials.
Benefits of Post-Secondary Education

Many turn to post-secondary education because it helps them move toward the career they really want—it’s a time to learn, grow, and plan for something better. It’s a worthwhile investment that opens doors to personal and professional opportunities. The various benefits of levelling up your learning may just be the greatest life-changing decision you’ll ever make.
Career Opportunities & Earnings
In Canada, studies indicate that post-secondary education offers a positive return on investment. The benefits—improved career prospects, higher earnings, and greater job security—make higher education a worthwhile choice. Pursuing post-secondary studies is one of the most effective ways to advance your career and boost your earning potential.
Here’s why investing in your education is worth it:
- Better Job Opportunities: One of the biggest motivations for going beyond high school is the promise of better career prospects. Post-secondary education can provide a broader selection of careers, which increases your chances of finding a job that suits your skills and ambitions.
- Stronger Employment Rates: In Canada, the employment rate for individuals aged 25–64 with a post-secondary education is approximately 85-89%, compared to just 72% for those with only a high school diploma.
- Higher Earning Potential: Education doesn’t just help you get a job—it can help you earn more. Data from the latest census confirms a strong link between education and earnings. Simply put, higher credentials typically lead to higher income.
- Long-Term Financial Success: Higher education continues to pay off over time. Beyond initial salary increases, the long-term financial success of post-secondary graduates includes job advancement, promotions, and greater lifetime earnings.
Pursuing post-secondary education not only helps you secure a job but also paves the way for long-term career advancement and financial growth.
Skill Development & Personal Growth
While post-secondary education is often associated with career advancement and higher earnings, its true value extends far beyond a paycheck. The benefits go deeper: post-secondary helps you to develop strong critical thinking, communication, and leadership skills that are essential for career success. These skills are built through:
- Critical Thinking: Through research projects, hands-on experience, and classroom discussions, you’ll learn to analyze problems and make informed decisions, a skill valued in fields like healthcare administration and business.
- Communication: Strong communication abilities are cultivated through presentations, professional writing, and team-based projects, preparing you for real-world interactions in hospitals, offices, and beyond.
- Leadership: Leadership development is another key focus, with opportunities to take charge of group work and engage in internships/practicums that build confidence and decision-making skills.
These competencies don’t just make you more employable—they help you adapt to change and able to advance in your career. Whether you’re working in a hospital, corporate office, or community organization, these skills set you up for long-term success long after you graduate.
Choosing the Right Institution
Selecting the right college or university is a crucial decision that can depend on a variety of personal and practical factors. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing a post-secondary institution in Canada:
Factors to Consider
Selecting the post-secondary institution is a big decision that depends on your career goals, learning preferences, and personal circumstances. Here are four key factors to consider when making your choice:
Job Placement Support & Industry Connections
Are you looking for a theoretical education or a post-secondary education that sets you up for career success. If the latter, look at an institution’s job placement rates, practicum programs, and employer partnerships. Colleges with strong industry ties often offer internships, work placements, and networking opportunities—a major advantage when entering the job market.
Program Flexibility & Duration
Consider whether you need part-time, full-time, or online study options. Some institutions offer accelerated programs that let you graduate faster, while others provide evening or weekend classes for working professionals.
Industry-Relevant Curriculum
A strong curriculum aligned with industry standards means you’ll gain practical, in-demand skills. Check for hands-on training, relevant industry recognition or accreditations, and up-to-date course content that match current job market needs.
By weighing these factors, you can choose a school that fits your ambitions and sets you up for success in your chosen field.
College vs. University
Choosing between college and university is a major decision that impacts your career path, finances, and learning experience. While both provide valuable education, they differ in program structure, cost, and career outcomes. Here’s what you need to know:
Career-Focused Training vs. Academic Pathways
Universities emphasize theoretical learning and research, ideal for careers requiring advanced study, such as law, medicine, or engineering. College programs, on the other hand, focus on hands-on, job-ready skills, which prepare you for technical, healthcare, and business professions where practical expertise is essential.
Return on Investment (ROI) & Cost Considerations
The rising cost of university tuition has led to concerns about return on investment. The Royal Bank of Canada (RBC) reports that tuition for undergraduate studies in Canada rose 12% between 2012 and 2017, while average graduate incomes increased by just 4% in the same period. This means that tuition has increased faster than the income you can earn with your degree, and as a result, the value of a degree has diminished.
Program Duration & Flexibility
- University degrees typically take 4 to 5 years to complete before you’re able to enter the job market – for instance, roles like teaching or nursing. Depending on your professional path, you may need to stay in school longer for fields like engineering (4-8 years) and medicine (8-10 years).
- Career college diplomas (6 months to a little over a year) and certificates (as short as 6–12 months) allow for faster workforce entry.
Learning Environment & Job Placement Support
Universities and colleges typically have larger classes and independent study, while colleges offer smaller class sizes, hands-on learning, and direct employer connections. Career-focused colleges often include practicums in industry settings and career services teams that provide resume, interview, and job search support to students, making it easier to be job-ready upon completion.
Both colleges and universities offer valuable career paths, but a degree isn’t the only route to success. With rising tuition costs, many opt for career-focused college programs that provide fast job placement and strong earning potential.
Online vs In-Person Learning
With the rise of educational technology and flexible learning options, you can choose between online and in-person learning—or even a mix of both. Each mode offers distinct advantages, but online learning stands out for its flexibility, making it an ideal choice for individuals balancing work, family, or other commitments.
Online Learning
Online education allows you to learn from anywhere, with no commuting costs. This makes it perfect for working professionals, parents, and international students who can’t relocate. Plus, there is the added convenience of having access to recorded lectures, virtual labs, and discussion forums. However, online learning requires strong self-discipline and lacks the in-person social and networking aspects of campus life.
In-Person Learning
Traditional learning fosters face-to-face interaction, hands-on training, and campus resources. It’s more important for practical programs like healthcare, trades, or lab-based sciences. However, it offers less flexibility and often comes with higher living and commuting costs.
While looking for post-secondary options, consider how each learning format fits your personal responsibilities, career goals, and preferred way of learning.
Common Myths About Post-Secondary Education
When planning your education, it’s important to separate fact from fiction. Let’s clear up a couple of these common myths.
Myth #1 – “You Need a University Degree to Be Successful”
This outdated idea ignores reality—many high-demand, well-paying careers don’t require a four-year degree. Business, healthcare, and IT professions can offer stable incomes, job security, and career advancement through career college programs. Tech fields are shifting, too, with many employers prioritizing skills over degrees.
Myth #2 – “College is Easier Than University”
Career colleges and universities have different teaching styles, but neither is inherently easier. Colleges focus on real-world applications, requiring students to complete hands-on projects, practicums, or skills assessments. Universities, on the other hand, emphasize research and academic writing. It depends on how you learn best and what career you want.
Choosing the right path depends on your goals, but what matters most is finding a program that prepares you for a rewarding future. While post-secondary education in Canada can provide multiple pathways to success, career colleges stand out for their hands-on, job-focused training that helps students enter the workforce quickly.
Whether you’re looking to gain industry-specific skills, switch careers, or advance in your field, career colleges offer flexible and practical programs designed to meet employer demands.
Thinking about your next step? Sundance College’s diploma programs are designed to guide you toward desirable and in-demand roles in today’s job market in sectors like education, healthcare, hospitality, law, and business. We focus on practical skills, industry-informed training, and support along the way—so you’re never on your own. Explore our diploma program options and contact us to find out how we can help you move forward with purpose.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Post-Secondary Education in Canada
Thinking about post-secondary education in Canada? Here are a few answers to some common questions:
-
What is meant by post-secondary education?
Post-secondary education refers to any education beyond high school. This includes colleges, universities, and polytechnics, where students can earn certificates, diplomas, degrees, or apprenticeships. Programs range from short-term training to multi-year university degrees, all designed to prepare students for the workforce.
-
How does post-secondary education help in career growth?
Post-secondary education expands job opportunities, increases earning potential, and builds essential skills. Those who have completed post-secondary credentials earn 65% more on average than someone with only a high school diploma. Career college graduates, in particular, enter the workforce faster and with job-ready skills, making them highly employable in fields like healthcare, business, and technology.
-
What’s the difference between a diploma and a degree?
A diploma is typically earned from a career college and takes six months to a little over a year. Rather than spending years in school, career colleges help you gain the skills to start working quickly in growing industries like healthcare, business, technology, law, hospitality, and supply chain management. A degree, on the other hand, is earned from a university and takes 4 to 5 years to be employable, offering a more academic and theoretical education. Degrees are necessary for professions like teaching (4-5 years), engineering (4-8 years), and medicine (8-10 years).
-
Can I study online in Canada?
Yes! Depending on your post-secondary institution of choice and type of program, you can study fully online or hybrid – perfect for students balancing work, family, or distance. Online programs provide the same credentials as in-person ones.
-
What is the difference between a certificate and a diploma?
A diploma program usually goes more in-depth than a certificate. Diplomas are designed to provide more in-depth knowledge and hands-on skills in a particular field and prepare you for a specific career. Certificates may focus on a particular skill set rather than prepare you for a career.
-
Diploma vs certificate: Which one is better?
It depends on your career goals! A certificate is fine for developing or strengthening a specific skill set. A diploma, on the other hand, provides a more comprehensive, hands-on education in your field—leading to broader job opportunities, stronger qualifications, and higher earning potential.
Related Blogs
Subscribe for more career advice
Blog Categories
Share on:
